建议改名游记.jpg
课程来源。
JSP
如果用Servlet动态回传html文件,那一行一行write,得写死程序员……
jsp的本质是servlet程序。第一次访问jsp页面的时候,服务器把jsp翻译成一个源文件编译成字节码。其实,底层就是把翻译出来的html一行一行回传。
jsp格式
每个生成的jsp页面开头都是page指令:
1
| <%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %>
|
还有一些属性:
autoFlush,设置当out输出流缓冲区满了之后是否自动刷新冲级区。默认值是true。
buffer属性,设置out缓冲区的大小。默认是8kb。
errorPage,出错时候自动跳转过去的页面。(这时候地址栏不变)
比如说加上一个errorPage="/error500.jsp",出现错误就显示error500.jsp了。
还有isErrorPage属性,顾名思义,默认false。true可以获取异常信息。
还可以导包导类……
甚至可以在里头写声明,形如<%! xxx %>。作用就是给翻译出来的java类定义属性、静态代码块、方法、内部类之类的。
就想这样:
1
2
3
4
5
| <%!
public int abc() {
return 12;
}
%>
|
主要用的还是输出表达式:
1
2
3
4
| <%=12 %> <br>/
<%=12.12 %> <br/>
<%="我是字符串" %> <br/>
<%=request.getParameter("username")%>
|
页面上就会显示12、12.12等等。
甚至可以写代码脚本:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
| <table border="1px">
<%
for (int i=0; i<10; i++) {
if (i%2==0) {
%>
<tr><td>第<%=i+1%>行奇</td></tr>
<%
} else {
%>
<tr><td>第<%=i+1%>行偶</td></tr>
<%
}
}
%>
</table>
|
jsp里头可以写html注释也可以写java注释。都会被翻译到对应的文件中。jsp注释是这样的<%--jsp注释--%>,不会被翻译。
域对象
pageContext,当前jsp页面范围内有效。
request,一次请求内有效。
session,一个会话范围内(有效打开浏览器访问服务器,直到关闭浏览器)
application,整个web工程范围内都有效只要web工程不停止,数据都在。
用的时候就request.setAttribute("key1", qwq);之类的。
用的时候最好从小到大用。
Session 生命周期
什么时候创建 session?当第一次调用 session 的时候。
什么时候销毁 session?过期或者 invalidate()(不是关闭浏览器之类的)
拿一个 HttpSessionListener 去监听。打开服务器,如果访问一个 html 文件,发现不会创建 session。因为 html 又不会调用 session。但是如果是一个 jsp 就会。因为 jsp 一般有个默认 session 对象。具体地:
- Servlet 调用 HttpServletRequest.getSession(true) 或者 HttpServletRequest.getSession() 这样的语句时;
- 若第一次访问某 Web 应用的一个 JSP 页面,且该页面的 page 指定的 Session 属性为 true,则服务器会自动为该页面分配一个 HttpSession 对象。
顺带一题,正常关闭服务器的时候并不会让所有 session 都消失。这些 session 会“钝化”,序列化地保存下来。重启服务器的时候活化。
标签
静态包含:
1
| <%@include file="/footer.jsp"%>
|
就可以了。footer.jsp就正常写。如果是html可能出现乱码,这个自己百度吧……
动态包含:
1
| <jsp:include page=""></jsp:include>
|
这个其实是把包含的jsp也翻译成java程序,然后传request、resopnse、out过去。
甚至可以加参数:
1
2
3
| <jsp:include page="/footer.jsp">
<jsp:param name="qwq" value="tql"/>
</jsp:include>
|
footer.jsp里头加一个<%=request.getParameter("qwq")%>。
请求转发
1
| <jsp:forward page=""></jsp:forward>
|
相当于request.getRequestDispatcher("xxx.jsp").forward(request, response)。
EL表达式
主要用来替换掉jsp输出,因为它太麻烦了……
1
2
| <% request.setAttribute("qwq", "orz"); %>
输出:${qwq}
|
可太方便了。还有它的值是null的时候输出的是空串,而不是n-u-l-l。查找的时候四个域对象从小到大来。
它也支持一些运算符,例如${3 > 5}就是false(>也可以换成gt这样的英文),还有&&逻辑与,%模之类的。除法是小数除法。
1
2
3
4
5
| <%
Map<String,Integer> map = new HashMap<String, Integer>();
request.setAttribute("map", map);
%>
输出:${empty map}
|
empty运算符,当后头的为null、空串、长度大小为0的list数组map之类的都是true。
当然也有三元运算符、点运算符、中括号运算符之类的。
隐含对象
取得四个域对象的信息,可以用xxxScope:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
| <%
pageContext.setAttribute("key", "pageContext");
request.setAttribute("key", "request");
session.setAttribute("key", "session");
application.setAttribute("key", "application");
%>
输出:${pageScope.key},${requestScope.key},${sessionScope.key},${applicationScope.key}
|
可以用${pageContext.request.serverName}之类的语句获得服务器地址。
还可以用param获得请求参数,paramValues获得一堆请求参数……不写了。
JSTL标签库
el表达式简化了输出,jstl标签库简化了脚本。
首先下载taglibs的impl和spec两个jar丢进去。
然后导入核心库:
1
| <%@taglib prefix="c" uri="http://java.sun.com/jsp/jstl/core"%>
|
也有前缀为fmt的格式库(后头改成fmt),前缀为fn的函数库(后头改成functions)。
set标签:
1
2
| <c:set scope="page" var="abc" value="123"/>
${pageScope.abc}
|
if标签(并没有else):
1
2
3
4
5
6
| <c:if test="${1>12}">
<h1>1大于12</h1>
</c:if>
<c:if test="${1<=12}">
<h1>1小于等于12</h1>
</c:if>
|
choose-when-otherwise(相当于switch)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
| <%
request.setAttribute("height", 123);
%>
<c:choose>
<%-- 只能用jsp注释 --%>
<c:when test="${requestScope.height > 130}">
<h1>130+</h1>
</c:when>
<c:when test="${requestScope.height > 120}">
<h1>120+</h1>
</c:when>
<c:otherwise>
<h1>小于等于120</h1>
</c:otherwise>
</c:choose>
|
伟大的forEach标签:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
| <table border="1">
<%-- var就是变量名字
varStatus可以让我们获得begin之类的属性。顺带一提还有一个步长step可以设置 --%>
<c:forEach begin="1" end="10" var="i" varStatus="status">
<tr>
<td>第${i}行,开始于${status.begin}</td>
</tr>
</c:forEach>
</table>
<%
request.setAttribute("arr", new String[]{"qwq", "orz", "tql"});
%>
<c:forEach items="${requestScope.arr}" var="item">
<h3>${item}</h3>
</c:forEach>
<%--也可以遍历map。输出的时候一个是entry.key一个是entry.value--%>
<%--甚至可以把items和begin、end结合起来--%>
|
文件上传下载
首先需要common-io和common-fileupload两个jar。
1
2
3
4
5
| <form action="http://localhost:8080/07_web_war_exploded/uploadFile" method="post" enctype="multipart/form-data">
用户名:<input type="text" name="username"/><br/>
图片:<input type="file" name="file"/><br/>
<button type="submit">提交</button>
</form>
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
| package com.poorpool.demo;
import org.apache.commons.fileupload.FileItem;
import org.apache.commons.fileupload.FileItemFactory;
import org.apache.commons.fileupload.disk.DiskFileItemFactory;
import org.apache.commons.fileupload.servlet.ServletFileUpload;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.List;
public class UploadFile extends HttpServlet {
@Override
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
if (ServletFileUpload.isMultipartContent(req)) {
FileItemFactory fif = new DiskFileItemFactory();
ServletFileUpload sfu = new ServletFileUpload(fif);
try {
List<FileItem> list = sfu.parseRequest(req);
for (FileItem item : list) {
if (item.isFormField()) {
System.out.println("表单项名" + item.getFieldName());
System.out.println("内容" + item.getString("UTF-8"));
} else {
System.out.println("表单项名" + item.getFieldName());
System.out.println("文件名" + item.getName());
item.write(new File(item.getName()));
}
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
|
下载则是这样的:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
| package com.poorpool.demo;
import org.apache.commons.io.IOUtils;
import javax.servlet.ServletContext;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
public class Download extends HttpServlet {
@Override
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
String fileName = "form.html";
ServletContext servletContext = getServletContext();
String mimeType = servletContext.getMimeType("/" + fileName);
System.out.println(mimeType);
resp.setContentType(mimeType);
resp.setHeader("Content-Disposition", "attachment; filename=" + fileName);
InputStream is = servletContext.getResourceAsStream("/" + fileName);
IOUtils.copy(is, resp.getOutputStream());
}
}
|
然而如果文件名带有中文会乱码(响应头只能是ascii),chrome使用URLEncoder.encode(文件名, "UTF-8")来代替setHeader那个fileName,但是火狐这么搞就是一坨百分号。firefox用base64编码。长这样:filename==?charset?B?xxxxx?=
其中charset换成编码(UTF-8),B是base64,xxx是内容。
一般用user-agent选择。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
| package com.poorpool.demo;
import org.apache.commons.io.IOUtils;
import javax.servlet.ServletContext;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.net.URLEncoder;
import java.util.Base64;
public class Download extends HttpServlet {
@Override
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
String fileName = "你好.html";
ServletContext servletContext = getServletContext();
String mimeType = servletContext.getMimeType("/" + fileName);
System.out.println(mimeType);
resp.setContentType(mimeType);
String ua = req.getHeader("User-Agent");
String addStr = "attachment; filename=";
if (ua.contains("Firefox")) {
addStr += "=?utf-8?B?" + new String(Base64.getEncoder().encode(fileName.getBytes("utf-8"))) + "?=";
} else {
addStr += URLEncoder.encode(fileName, "utf-8");
}
resp.setHeader("Content-Disposition", addStr);
InputStream is = servletContext.getResourceAsStream("/" + fileName);
IOUtils.copy(is, resp.getOutputStream());
}
}
|
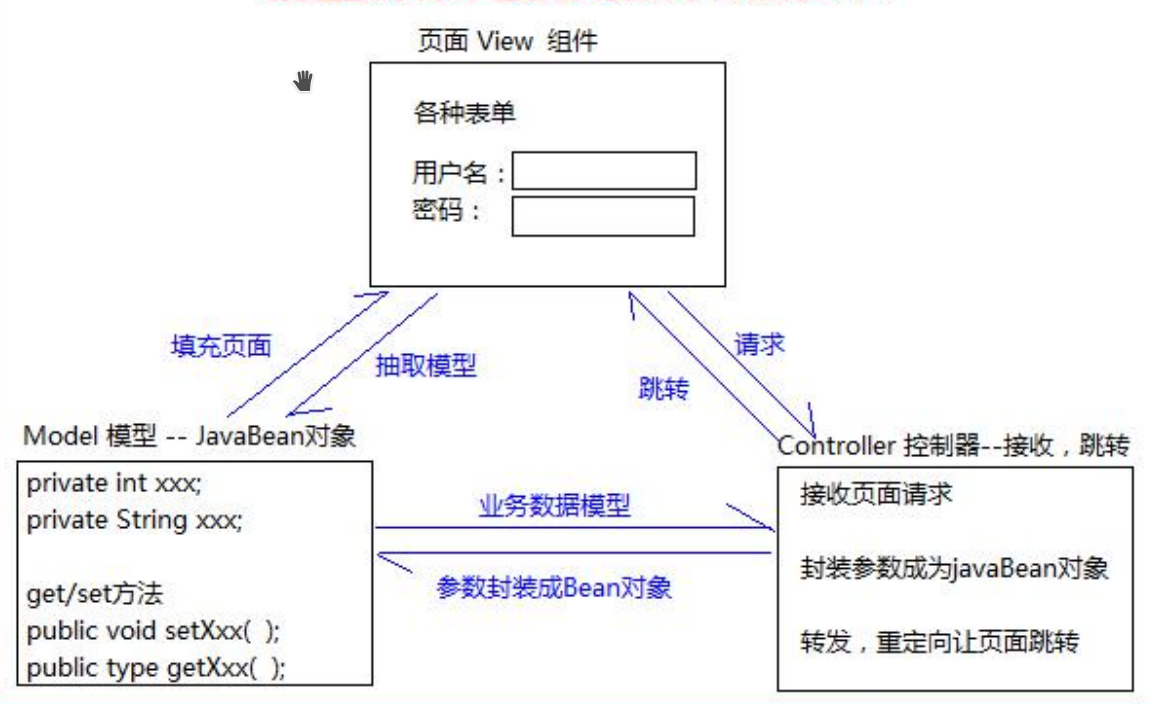
MVC
模型、视图、控制器。可以理解为model是javabean,视图是jsp/html,控制器是servlet。
COOKIE
是服务器通知客户端保存键值对的手段。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
| public class CookieServlet extends BaseServlet {
protected void createCookie(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
Cookie cookie1 = new Cookie("key1", "value1");
resp.addCookie(cookie1);
resp.getWriter().print("Cookie创建成功");
}
}
|
BaseServlet是重写了doPost/doGet用反射调用方法的抽象类,自己写的。
获得(浏览器请求中的)cookie的话,用req.getCookies()获得Cookie[]数组。每个cookie都有getName()和getValue()方法。
修改的话,直接创建一个同名Cookie对象或者是获得了Cookie对象然后setValue(),然后都要addCookie(yourcookie)通知浏览器修改。
顺带一提,cookie的内容要求挺严格。要是有空格逗号中文之类的建议用BASE64编码。
生命控制使用setMaxAge(),正值是指定秒数以后过期,0是立刻删除,负值是关闭浏览器以后删除。
可以设置路径,只有在路径底下cookie才有效
1
| cookie.setPath( req.getContextPath() + "/abc" );
|
例如:成功登录以后记录下来用户名这样下一次登录就不用输入用户名了:
1
2
3
4
5
| <form action="loginServlet" method="post">
用户名:<input type="text" name="username" value="${cookie.username.value}"/><br/>
密码:<input type="password" name="password" value=""/><br/>
<button type="submit">提交</button>
</form>
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
| public class LoginServlet extends HttpServlet {
@Override
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
String username = req.getParameter("username");
String password = req.getParameter("password");
if ("admin".equals(username) && "admin".equals(password)) {
Cookie user = new Cookie("username", username);
user.setMaxAge(60 * 60 * 24 * 7);
resp.addCookie(user);
resp.getWriter().write("login successed");
} else {
resp.getWriter().write("login failed");
}
}
}
|
Session
Session 是一个接口,是会话,是用来维护一个客户端和服务器之间关联的一种技术。每个客户端都有自己的一个Session会话。
Session会话中,我们经常用来保存用户登录之后的信息。
创建Session:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
| protected void createOrGetSession(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
HttpSession session = req.getSession();
boolean isNew = session.isNew();
String id = session.getId();
resp.getWriter().write("得到的session id " + id + "<br/>新创建?" + isNew);
}
|
session也是域,可以在java代码中session.setAttribute(“key1”, “value1”),也可以在jsp中用${sessionScope.key1}之类的东西。
关于寿命:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
| protected void defaultLife(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
HttpSession session = req.getSession();
System.out.println(session.getMaxInactiveInterval());
session.setMaxInactiveInterval(60*60);
session.invalidate();
}
|
要调整默认时间,在自己的web.xml里头写。
至于Session和Cookie:


