课程来源
基础部分
声明变量除了 var,还有 let 和 const。推荐使用后两者。let 有块级作用域。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
| <!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
<script src="../js/vue.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
<h1>{{ message }}</h1>
<h1 v-once>{{ message }}</h1>
<h1>{{ link }}</h1>
<h1 v-html="link"></h1>
<ul>
<li v-for="item in movies">{{ item }}</li>
</ul>
<h1>counter</h1>
<p>计数器值为:{{ counter }}</p>
<p>
<button @click="increment">+</button>
<button v-on:click="counter--">-</button>
</p>
</div>
<script>
const app = new Vue({
el: "#app",
data: {
message: "Hello",
movies: ['movie1', 'movie2'],
counter: 0,
link: "<a href='http://www.baidu.com'>link</a>"
},
methods: {
increment() {
this.counter++;
},
decrement() {
this.counter--;
}
}
});
</script>
</body>
</html>
|
在控制台改变 app.message = "xxx" 页面也会直接变化。加上 v-once 不会,此时元素和组件只会渲染一次。
mvvm:model、view、view model。
v-pre 会跳过自己和子元素的编译过程,直接显示本来的东西,例如直接显示 {{ message }}。
如果渲染时间很长,会让用户看到 {{ message }} 这种鬼畜东西,非常不好。拿个 v-cloak(斗篷)覆盖住(好像也没啥用)。vue 解析之前有这个属性,解析之后没有。所以给有这个属性的都不显示:
1
2
3
4
5
| <style>
[v-cloak] {
display: none;
}
</style>
|
v-bind
动态绑定属性。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
| <!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
<script src="../js/vue.js"></script>
<style>
[v-cloak] {
display: none;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
<img v-bind:src="imgUrl"/>
</div>
<script>
const app = new Vue({
el: "#app",
data: {
imgUrl: "https://ss2.bdstatic.com/70cFvnSh_Q1YnxGkpoWK1HF6hhy/it/u=649740401,4107288271&fm=26&gp=0.jpg"
}
});
</script>
</body>
</html>
|
v-bind 绑定 class 怎么做?显然不能和上面的 imgUrl 一样写个什么东西放在 data 里头或者是 在 computed 里头写一个函数。可以考虑使用一个 string-bool 的类,称为对象语法。true 的话就把类加上,false 就不把类加上。总的来说,就是通过修改 bool 值来修改 class。还有数组语法,用得少。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
| <!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
<script src="../js/vue.js"></script>
<style>
.active {
color: red;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
<div v-bind:class="{active: isActive, line: isLine}">div</div>
<div v-bind:class="getClasses()">div</div>
<button @click="btnClick">switch color</button>
</div>
<script>
const app = new Vue({
el: "#app",
data: {
isActive: true,
isLine: false
},
methods: {
btnClick: function () {
this.isActive = !this.isActive;
},
getClasses: function () {
return {active: this.isActive, line: this.isLine}
}
}
});
</script>
</body>
</html>
|
此时甚至可以在控制台通过控制 app.isActive 直接控制颜色的变化。
v-bind 控制 style 的话也有对象语法和数组语法。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
| <div id="app">
<div v-bind:style="{fontSize: finalSize, color: 'red'}">div</div>
</div>
<script>
const app = new Vue({
el: "#app",
data: {
finalSize: '100px'
}
});
</script>
|
计算属性
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
| <div id="app">
<div>{{ fullName }}</div>
</div>
<script>
const app = new Vue({
el: "#app",
data: {
firstName: "qwq",
lastName: "orz"
},
computed: {
fullName: function () {
return this.firstName + " " + this.lastName;
}
}
});
</script>
|
计算属性有 getter 和 setter,默认没有 setter 也就是只读属性。计算属性只有当开始或值变化的时候才会计算一次,是有缓存的。
杂项
v-on:click="funcName" 看起来像不传参数,其实会传一个 event 当参数。但是如果传参,就不会传这个事件。又有自己的参数又有时间,就 funcName(123, $event) 就行了。
.stop 可以阻止事件冒泡,.prevent 可以阻止默认事件,.once 确保执行一次……
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
| <div id="app">
<div v-if="score>=90">优秀</div>
<div v-else-if="score>=60">及格</div>
<div v-else>不及格</div>
</div>
<script>
const app = new Vue({
el: "#app",
data: {
score: 81
}
});
</script>
|
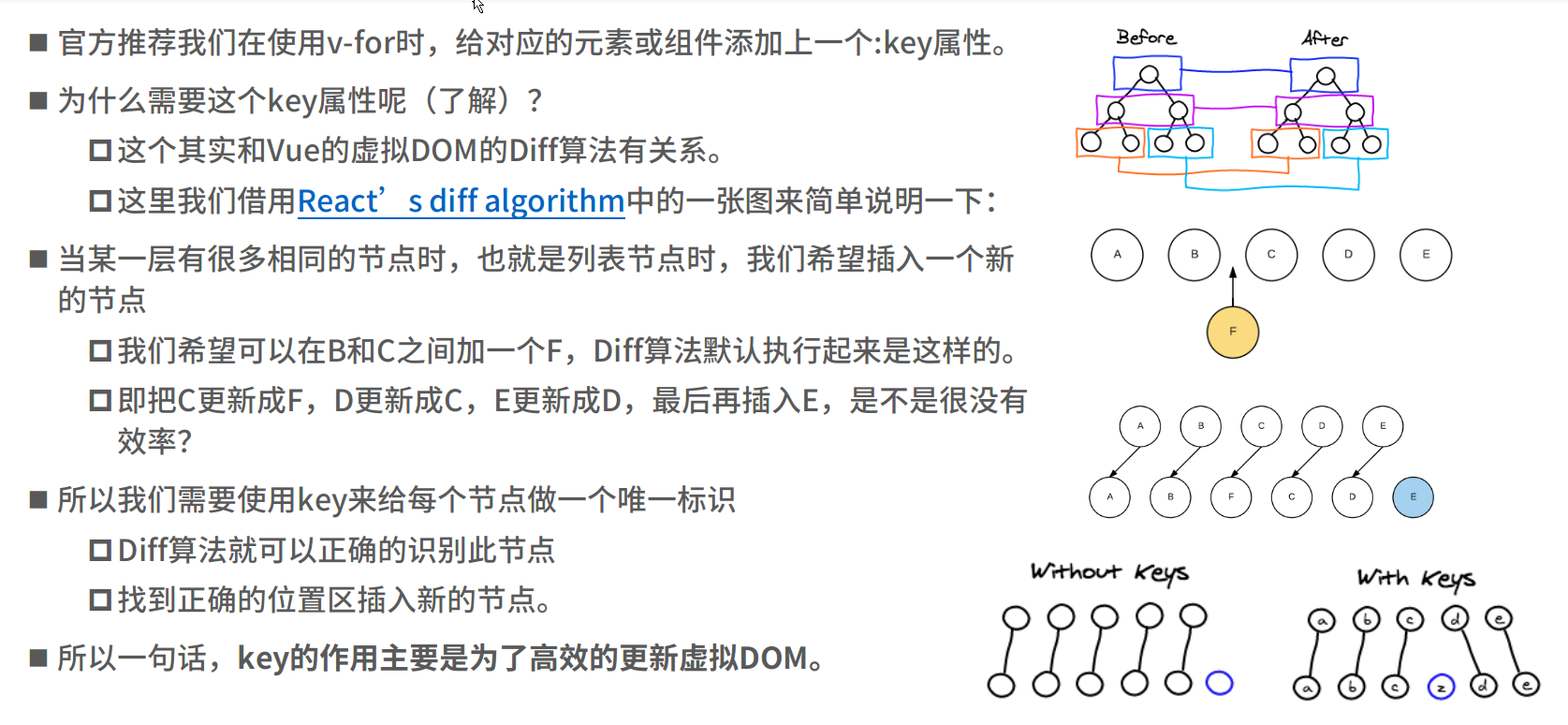
关于 input 复用问题,可以加属性 key(过 于 抽 象)。
v-if 和 v-show 当条件都为 false 的时候都不会显示,但是 v-if 压根不会渲染,v-show 只是将 display 设为 none。隐藏显示切换频繁用 v-show,否则使用 v-if。
v-for 遍历数组可以同时加上 index,例如 v-for="(item, index) in movies" 之类的。也可以遍历一个对象,输出 key value等等。
过滤器
在 filters 中写上,然后在 mustache 语法里头写一个 | 传给它就行了,就像是 pipe。
1
2
3
4
5
| filters: {
showPrice(price) {
return "¥" + price.toFixed(2);
}
}
|
1
| <td>{{ item.price | showPrice}}</td>
|
js 函数式编程
filter、map、reduce:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
| const nums = [1, 5, 10, 67, 102, 707];
let qwq = nums.filter(function (n) {
return n < 100;
});
console.log(qwq);
let qwq2 = qwq.map(function (n) {
return n * 2;
});
console.log(qwq2);
let qwq3 = qwq2.reduce(function (preValue, n) {
return preValue + n;
}, 0);
console.log(qwq3);
let qwq4 = qwq.filter(n => n < 100).map(n => n * 2).reduce((preValue, n) => preValue + n);
console.log(qwq4);
|
也可以连起来写。
v-model
实现表单和数据的双向绑定。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
| <body>
<div id="app">
<form>
<input type="text" v-model="message">
</form>
<h1>{{ message }}</h1>
</div>
<script>
const app = new Vue({
el: "#app",
data: {
message: "message"
}
});
</script>
</body>
|
修改数据和表单的任意一个,另一个也会变化。
v-model 有一些修饰符,比如加上 .lazy 不会立刻变化,.number(类型是数字)。
组件
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
| <!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
<script src="../js/vue.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
<cpn1></cpn1>
</div>
<script>
const cpnC2 = Vue.extend({
template: `
<div>
<h1>子组件</h1>
</div>
`
});
const cpnC1 = Vue.extend({
template: `
<div>
<h1>父组件</h1>
<cpn2></cpn2>
</div>
`,
components: {
cpn2: cpnC2
}
});
// 可以注册成全局组件,每个 Vue 实例都能用
const app = new Vue({
el: "#app",
components: {
cpn1: cpnC1//局部组件。在 #app 中只能使用 cpn1,不能使用 cpn2。要使用的话要把 cpn2 也注册上。
}
});
</script>
</body>
</html>
|
关于语法糖,Vue.component 可以注册全局组件,局部组件可以直接在上头的 cpn1 冒号后头放 cpn2 那个 extend 的参数。template 可以抽离。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
| <body>
<div id="app">
<cpn></cpn>
</div>
<template id="cpn">
<h1>{{ title }}</h1>
</template>
<script>
Vue.component("cpn", {
template: "#cpn",
data() {
return {
title: "qwqwq"
}
}
});
const app = new Vue({
el: "#app"
});
</script>
</body>
|
子组件取得父组件的数据,使用 props:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
| <body>
<div id="app">
<cpn :cmessage="message" :cmovies="movies"></cpn>
</div>
<template id="cpn">
<div>
<h1>{{ cmessage }}</h1>
<p>{{ cmovies }}</p>
</div>
</template>
<script type="text/javascript">
const cpn = {
template: "#cpn",
props: ['cmessage', 'cmovies']
}
const app = new Vue({
el: "#app",
data: {
message: "hello",
movies: ['a', 'b', 'c']
},
components: {
cpn
}
});
</script>
</body>
|
子组件向父组件传递事件:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
| <body>
<div id="app">
<cpn @qwq="fatherclick"></cpn>
</div>
<template id="cpn">
<div>
<button v-for="item in movies" @click="childclick(item)">{{ item }}</button>
</div>
</template>
<script>
const cpn = {
template: "#cpn",
data() {
return {
movies: ['a', 'b', 'c']
}
},
methods: {
childclick(item) {
console.log("child function ", item);
this.$emit('qwq', item);
}
}
}
const app = new Vue({
el: "#app",
components: {
cpn
},
methods: {
fatherclick(item) {
console.log("father function ", item);
}
}
});
</script>
</body>
|
props 得到的数据最好不要用于 v-model 双向绑定。在 data 里头再写一个。父组件方法里头可以用 this.$children 得到子组件的数组。使用 this.$refs 获得设置了 ref 属性的组件们,以 json 对象的形式。子组件用 this.$parent 获得父组件,但要避免访问父组件数据。
