杂项
国际化
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
| package com.poorpool.demo;
import java.text.MessageFormat;
import java.util.Locale;
import java.util.ResourceBundle;
public class HelloDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
ResourceBundle resourceBundle = ResourceBundle.getBundle("com.poorpool.resource.Ds", Locale.US);
String str = resourceBundle.getString("hello.msg");
System.out.println(MessageFormat.format(str, "poorpool"));
}
}
|
ThreadLocal
先来看一段明显错误
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
| package com.poorpool.demo;
class Message {
private String content;
public String getContent() {
return content;
}
public void setContent(String content) {
this.content = content;
}
}
class Resource {
public static Message message;
}
class MessagePrint {
public static void print() {
System.out.println(Resource.message.getContent());
}
}
public class HelloDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
String[] vals = new String[]{"poorpool", "thank", "you"};
for(String val : vals) {
new Thread(()->{
Resource.message = new Message();
Resource.message.setContent(val);
MessagePrint.print();
}).start();
}
}
}
|
输出全是you。
用ThreadLocal每个线程就能保存自己的东西:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
| package com.poorpool.demo;
class Message {
private String content;
public String getContent() {
return content;
}
public void setContent(String content) {
this.content = content;
}
}
class Resource {
public static final ThreadLocal<Message> MESSAGES = new ThreadLocal<>();
}
class MessagePrint {
public static void print() {
System.out.println(Resource.MESSAGES.get().getContent());
}
}
public class HelloDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
String[] vals = new String[]{"poorpool", "thank", "you"};
for(String val : vals) {
new Thread(()->{
Resource.MESSAGES.set(new Message());
Resource.MESSAGES.get().setContent(val);
MessagePrint.print();
}).start();
}
}
}
|
Timer类
干守护线程类似的任务。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
| package com.poorpool.demo;
import java.util.Timer;
import java.util.TimerTask;
class TimeThread extends TimerTask {
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println("定时任务");
}
}
public class HelloDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Timer timer = new Timer();
timer.schedule(new TimeThread(), 1000, 2000);
}
}
|
schedule方法有挺多,可以看看。
流
OutputStream字节输出流
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
| package com.poorpool.demo;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.OutputStream;
public class HelloDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
File file = new File("oicode" + File.separator + "20200515" + File.separator + "qwq.txt");
if(!file.getParentFile().exists())
file.getParentFile().mkdirs();
OutputStream output = new FileOutputStream(file);
output.write("yxchen.net\n".getBytes());
output.close();
}
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
| package com.poorpool.demo;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.InputStream;
public class HelloDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
File file = new File("qwq.cpp");
try(InputStream inputStream = new FileInputStream(file)) {
StringBuffer buffer = new StringBuffer();
byte[] bytes = new byte[10];
int len = 0;
while((len=inputStream.read(bytes, 0, 10))>=0)
buffer.append(new String(bytes, 0, len));
System.out.println(buffer);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
|
Writer字符输出流
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
| package com.poorpool.demo;
import java.io.*;
public class HelloDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
File file = new File("qwq.txt");
try(Writer writer = new FileWriter(file)) {
writer.write("poorpool\n");
writer.write("hello!\n");
writer.append("qwq\n").append("233\n");
}
catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
|
Reader字符输入流
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
| package com.poorpool.demo;
import java.io.*;
public class HelloDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
File file = new File("qwq.txt");
try(Reader reader = new FileReader(file)) {
char []data = new char[5];
StringBuffer buffer = new StringBuffer();
int len = 0;
while((len=reader.read(data, 0, 5))>=0)
buffer.append(data, 0, len);
System.out.println(buffer);
}
catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
|
字节流和字符流的区别
因为字节流是字节,字节输出流便可以直接与目标介质进行输出控制。字符流要有一个内存缓冲区,flush一下才会写入目标介质。具体地,写了不close,字节输出流的文件有东西,字符输出流的文件没东西。中文主要用字符输出流。
转换流
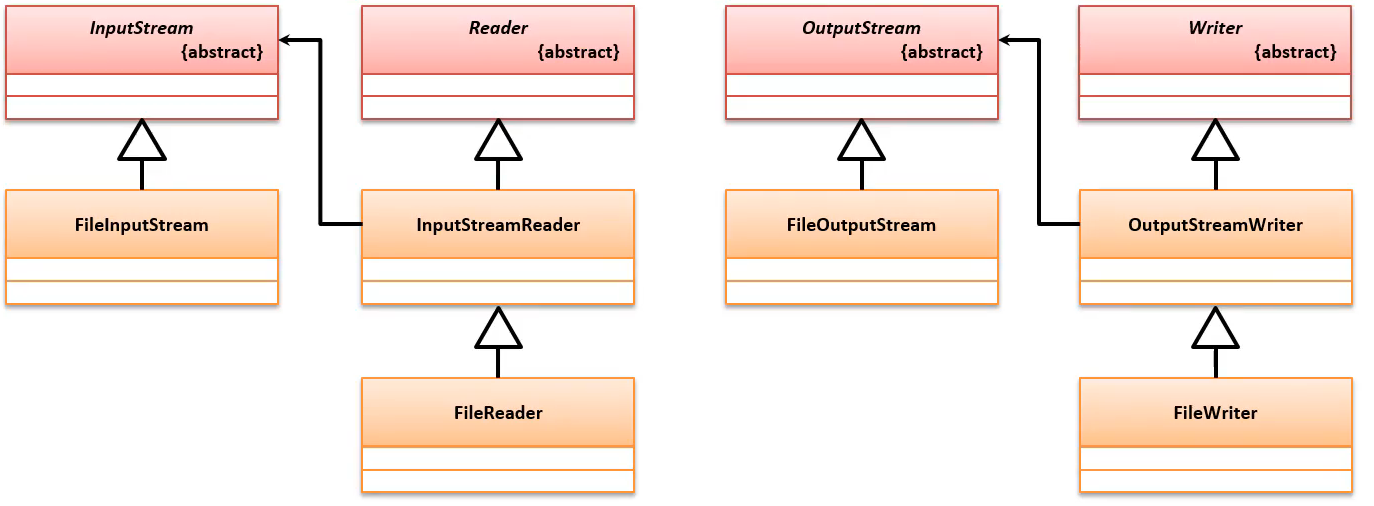
顺带提一下transferTo。这样能很轻松实现文件复制。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
| package com.poorpool.demo;
import java.io.*;
public class HelloDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
InputStream inputStream = new FileInputStream(new File("cpt1-1.png"));
OutputStream outputStream = new FileOutputStream(new File("qwq.png"));
inputStream.transferTo(outputStream);
}
}
|
内存流
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
| package com.poorpool.demo;
import java.io.*;
public class HelloDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
InputStream input = new ByteArrayInputStream("poorpool".getBytes());
OutputStream output = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
int data = 0;
while((data = input.read())>=0) {
output.write(Character.toUpperCase(data));
}
System.out.println(output);
input.close();
output.close();
}
}
|
还有管道流,用于多线程or进程之间的输入输出。这个不写了。
RandomAccessFile
实现文件的随机读取。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
| package com.poorpool.demo;
import java.io.*;
public class HelloDemo {
public static final int MAX_LENGTH=10;
public static String addEscape(String x) {
StringBuffer buffer = new StringBuffer(x);
while(buffer.length()<MAX_LENGTH)
buffer.append(" ");
return buffer.toString();
}
public static void writes() {
File file = new File("qwq.txt");
try(RandomAccessFile raf = new RandomAccessFile(file, "rw")) {
String[] names = new String[]{"poorpool", "qwq", "qaq"};
int[] ages = new int[]{12, 2, 999};
for(int i=0; i<names.length; i++) {
raf.write(addEscape(names[i]).getBytes());
raf.writeInt(ages[i]);
}
}
catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public static void reads() {
File file = new File("qwq.txt");
try(RandomAccessFile raf = new RandomAccessFile(file, "r")) {
raf.skipBytes(MAX_LENGTH+4);
byte[] data = new byte[MAX_LENGTH];
raf.read(data);
System.out.println(new String(data).trim());
System.out.println(raf.readInt());
}
catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
writes();
reads();
}
}
|
打印流
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
| package com.poorpool.demo;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.PrintWriter;
public class HelloDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
File file = new File("qwq.txt");
PrintWriter pw = new PrintWriter(new FileOutputStream(file));
pw.println(10);
pw.printf("hello %s, your age is %d\n", "porp", 16);
pw.close();
}
}
|
Scanner
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
| package com.poorpool.demo;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class HelloDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
scanner.useDelimiter("\n");
while(scanner.hasNext())
System.out.println(scanner.next());
}
}
|
这个最好使。不行就BufferReader。
输出可以考虑PrintWriter。
序列化
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
| package com.poorpool.demo;
import java.io.*;
class Book implements Serializable {
private String name;
private String author;
private double price;
public Book(String name, String author, double price) {
this.name = name;
this.author = author;
this.price = price;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Book{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", author='" + author + '\'' +
", price=" + price +
'}';
}
}
public class HelloDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(new File("qwq.txt")));
oos.writeObject(new Book("qwq", "orz", 2.33));
oos.close();
ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream(new File("qwq.txt")));
Book book = (Book)ois.readObject();
System.out.println(book);
}
}
|
不过,像是总价=单价*数量就没有必要序列化,可以用transient关键字。
网络编程
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
| package com.poorpool.server;
import java.io.PrintStream;
import java.net.ServerSocket;
import java.net.Socket;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class ServerDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
ServerSocket sers = new ServerSocket(9999);
Socket sock = sers.accept();
PrintStream ps = new PrintStream(sock.getOutputStream());
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(sock.getInputStream());
while(true) {
if(scanner.hasNext()) {
String qwq = scanner.next();
System.out.println("Get " + qwq);
if(qwq.equalsIgnoreCase("exit")) {
break;
}
ps.println(qwq);
}
}
sock.shutdownOutput();
sers.close();
}
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
| package com.poorpool.client;
import java.io.PrintStream;
import java.net.Socket;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class ClientDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Socket sock = new Socket("localhost", 9999);
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(sock.getInputStream());
PrintStream out = new PrintStream(sock.getOutputStream());
Scanner scanner1 = new Scanner(System.in);
while(true) {
String qwq = scanner1.nextLine();
out.println(qwq);
System.out.println("waiting...");
if (scanner.hasNext()) {
String ret = scanner.next();
System.out.println("Echo: " + ret);
}
if(qwq.equalsIgnoreCase("exit"))
break;
}
sock.close();
}
}
|
Java里头有ServerSocket和Socket,挺方便的。
多线程也好处理,每次accept一个client的socket就把它扔进一个Runnable里头跑起来。
也可以使用udp的socket。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
| package com.poorpool.server;
import java.net.DatagramPacket;
import java.net.DatagramSocket;
public class ServerDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
DatagramSocket client = new DatagramSocket(9999);
byte[] data = new byte[1024];
DatagramPacket packet = new DatagramPacket(data, data.length);
client.receive(packet);
System.out.println(new String(data, 0, packet.getLength()));
client.close();
}
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
| package com.poorpool.client;
import java.net.DatagramPacket;
import java.net.DatagramSocket;
import java.net.InetAddress;
public class ClientDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
DatagramSocket server = new DatagramSocket(9998);
String msg = "poorpool";
DatagramPacket packet = new DatagramPacket(msg.getBytes(), 0, msg.length(), InetAddress.getByName("localhost"), 9999);
server.send(packet);
server.close();
}
}
|
